
Dev Containers are a kind of containers that allows you to use containers for development, a Dev Container serve as a development enviroment with all dependencies and libraries needed to run your apps, thus, you can isolate the libraries from the base system and avoid conflicts for your project.
Keeping the promise of containers; the workspace are originally in the local file system and cloned in the container workspace, also you can install and run extensions and share the development configuration enviroment between different containers.

Install Dev Container Extension in VSCode
Before using Dev Containers with your IDE you must have Docker installed in your computer or remotely.
After that, to enble the Dev Containers for VSCode, go to the extensions button (Ctrl + Shift + X) type “Dev containers” and then install it.
Using GitHub.
You can use Git and GitHub with Dev Containers in VSCode, I suggest first create the repo and pull locally, then the container will have the credentials (if needed).
Create your First Dev Container.
I am assuming for this tutorial, that you already have the source code of the project in your computer and you want to use/migrate Dev Containers to manage your project enviroment; so, just follow up the steps below:
-
- Open your project in VSCode from the menu, in case your project is in WSL you can use command line and then open VSCode:
Bash
$ cd your/path/project
$ code .
-
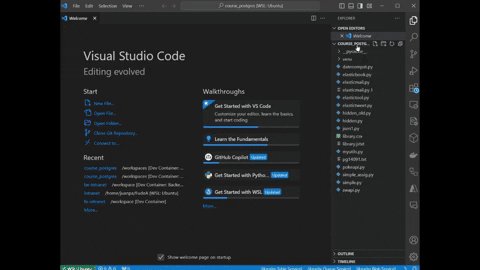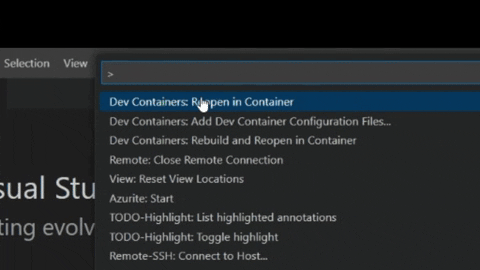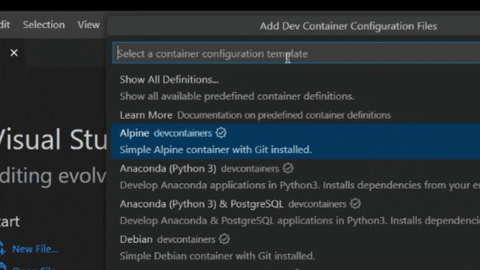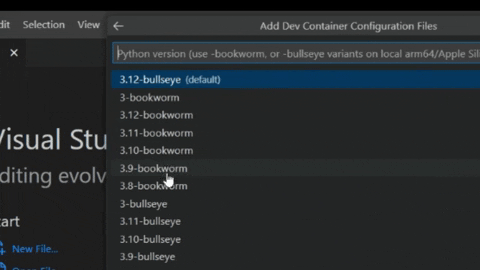
- Run the command: >
Dev Containers: Reopen in Containerwith F1 key
- Run the command: >

-
- Then, you will get a list of available containers for your project, Type the language of your project, when you select it, you will get a sorted list with the versions, select what you want to use in your project.
-
- When creating the new Dev container, VSCode will reload and then, inside the project will be the folder .devcontainer/ with the file inside devcontainer.json
When the buid process finish you can browse through the source code of your project and make changes, add folders and files that will be in your local filesystem too.
You can close VSCode and when you open the project again, it will start the container with the source code and the full enviroment to continue working.
Besides the default container you can install other features at build process or add later in devcontainer.json file


